-
Download:
My Results |
All BMPs
Constructed (Treatment) Wetlands
 This 12-acre constructed wetland provides wildlife habitat for migrating waterfowl and a nesting area for animals. Photographer: Jason Johnson. Photo Courtsey of USDA NRCS.
This 12-acre constructed wetland provides wildlife habitat for migrating waterfowl and a nesting area for animals. Photographer: Jason Johnson. Photo Courtsey of USDA NRCS.
Practice Type: Structural
Climatic Zones: Temperate, Semiarid, Tropical
Regions: North America, Europe, South America, South Asia, Africa
Pollutants Treated: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sediment
N Efficiency1: 40-43%
P Efficiency1: 59%
S Efficiency1: 75%
Description: Constructed wetlands, sometimes called treatment wetlands, are man-made systems engineered to approximate the water-cleaning process of natural wetlands. These artificial wetlands capture and filter runoff from cropland, feedlots, aquaculture operations, agricultural processing facilities, and urban stormwater. They effectively remove excess nutrients, sediment and other pollutants from surface runoff. 2
Implementation Considerations: Constructed wetlands will require land to be taken out of production, but agroforestry and water-based crops for fiber, food, and fodder can partially offset these costs. In an urban context applicability of this BMP will depend on availability of suitably sited land. In an aquaculture context, wetlands are not suitable for treating the entire volume of an aquaculture pond because of the need to retain water for at least two days, but this option may be appropriate to treat the concentrated effluents typically associated with the final 10 percent to 20 percent of pond volume during draining. Implementation costs can be high and maintenance costs for constructed wetlands can be substantial. Over long term, wetlands can be very cost effective for reducing nutrients if properly designed and maintained.
Scalable to small farms? Yes
1 Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.
2 Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.; 17. "EU Database of Best Practices." Living Water Exchange: Promoting Replication of Good Practices for Nutrient Reduction and Joint Collaboration in Central and Eastern Europe. Web. Sept. 2013. http://nutrient2.iwlearn.org/nutrient-reduction-practices/eu-database-of-practices/view.
Continuous No-Till/Zero Till/Direct Seeding (Conservation Tillage)
Category: Erosion Control
Practice Type: Management
Landuse/Agriculture Type: Row Crop, Small Grains
Climatic Zones: Temperate, Semiarid, Tropical
Regions: North America, Europe, South Africa, Asia
Pollutants Treated: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sediment
N Efficiency1: 10-15%
P Efficiency1: 20-40%
S Efficiency1: 70%
Description: Continuous no-till, or zero till, is the most effective version of conservation tillage. As with other conservation tillage systems, no-till systems leave greater than 30% (and often up to 70%) of crop residue on the field. Planting is the only operation that disturbs the soil. Direct seeding is a method of planting that is increasingly used in no-till systems. Direct seeding uses narrow knives, single discs or double discs to open narrow strip of soil between openers for the seed bed, retaining nearly the entire residue on the surface. No-till systems provide the least soil disturbance of all conservation tillage systems. Maintaining residues on the field minimizes soil erosion and runoff. 2
Implementation Considerations: For best results, fertilizers should be injected or banded. This is particularly true for nitrogen, especially for those forms that are volatile. Weed control is primarily dependent upon herbicides. The soil warms up more slowly in the spring with no-till than it does with conventional tillage.
Scalable to small farms? Yes
1 "Documentation: Source Data, BMP Effectiveness Values." Chesapeake Assessment Scenario Tool. Web. 2013. http://casttool.org/Documentation.aspx .
2 Estimates of County-level Nitrogen and Phosphorus Data for Use in Modeling Pollutant Reduction Documentation for Scenario Builder Version 2.2." Chesapeake Bay. Dec. 2010. Web. May 2013. http://archive.chesapeakebay.net/pubs/SB_V22_Final_12_31_2010.pdf.
Practice Type: Management
Landuse/Agriculture Type: Row Crop, Small Grains
Climatic Zones: Temperate, Semiarid, Tropical
Regions: North America, Europe, South Africa, Asia
Pollutants Treated: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sediment
N Efficiency1: 10-15%
P Efficiency1: 20-40%
S Efficiency1: 70%
Description: Continuous no-till, or zero till, is the most effective version of conservation tillage. As with other conservation tillage systems, no-till systems leave greater than 30% (and often up to 70%) of crop residue on the field. Planting is the only operation that disturbs the soil. Direct seeding is a method of planting that is increasingly used in no-till systems. Direct seeding uses narrow knives, single discs or double discs to open narrow strip of soil between openers for the seed bed, retaining nearly the entire residue on the surface. No-till systems provide the least soil disturbance of all conservation tillage systems. Maintaining residues on the field minimizes soil erosion and runoff. 2
Implementation Considerations: For best results, fertilizers should be injected or banded. This is particularly true for nitrogen, especially for those forms that are volatile. Weed control is primarily dependent upon herbicides. The soil warms up more slowly in the spring with no-till than it does with conventional tillage.
Scalable to small farms? Yes
1 "Documentation: Source Data, BMP Effectiveness Values." Chesapeake Assessment Scenario Tool. Web. 2013. http://casttool.org/Documentation.aspx .
2 Estimates of County-level Nitrogen and Phosphorus Data for Use in Modeling Pollutant Reduction Documentation for Scenario Builder Version 2.2." Chesapeake Bay. Dec. 2010. Web. May 2013. http://archive.chesapeakebay.net/pubs/SB_V22_Final_12_31_2010.pdf.
Contour Buffer Strips
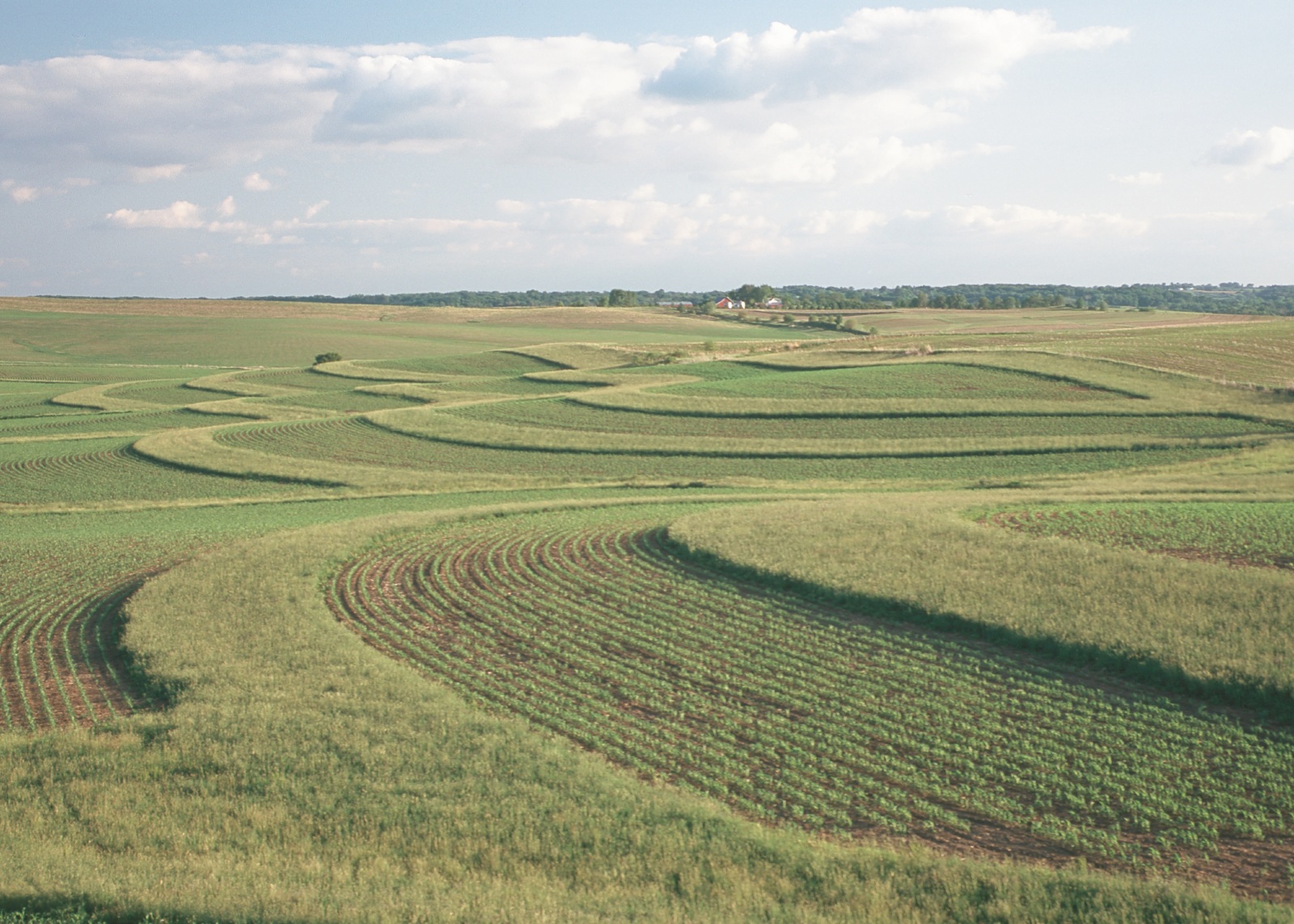 Grassed contour buffer strips cover an entire field in Tama County, Iowa. Photographer: Lynn Betts. Photo Courtsey of USDA NRCS.
Grassed contour buffer strips cover an entire field in Tama County, Iowa. Photographer: Lynn Betts. Photo Courtsey of USDA NRCS.
Practice Type: Structural
Landuse/Agriculture Type: Row Crop
Climatic Zones: Temperate
Regions: North America, Europe, South Africa
Pollutants Treated: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sediment
S Efficiency1: 87%
Description: Contour buffer strips are permanent, narrow bands of grasses/legumes planted on the contour (across or perpendicular to a slope) between wider strips of crops farmed on the contour. Contour buffers are designed to reduce soil erosion and runoff on sloped fields by slowing the flow of water in areas prone to sheet and rill erosion. Buffer strips can also provide pollutant removal to shallow groundwater flow that interacts with the buffer root zone. 2
Implementation Considerations: Contour buffer strips are most suitable for uniform 4% to 8% slopes and where rainfall intensity is low to moderate. And the cost of contour buffer strips is dependent upon value of the land taken out of production, buffer installation, plant establishment, and maintenance.
Scalable to small farms? Yes
1 Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.; "Contour Buffer Strips." Natural Resources Conservation Service, Conservation Practice Standard. Web. Jan. 2014. http://www.awqa.org/pubs/conservation/NRCSPractices/ContourBufferStrips.pdf.
2 Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.; "Contour Buffer Strips." Natural Resources Conservation Service, Conservation Practice Standard. Web. Jan. 2014. http://www.awqa.org/pubs/conservation/NRCSPractices/ContourBufferStrips.pdf.
Contour Farming
Category: Erosion Control
Practice Type: Structural, Management
Landuse/Agriculture Type: Row Crop, Small Grains, Fodder
Climatic Zones: Temperate, Semiarid, Tropical
Regions: North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia
Pollutants Treated: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sediment
Description: Contour farming entails farming along the contour such that ridges, furrows and planting are perpendicular to the slope of the land. The rows running across the slope are designed to be as level as possible to facilitate tillage and planting operations on the contour. Contour farming is an erosion control system that has the effect of increasing infiltration of rainwater and reducing sheet and rill erosion, thereby reducing soil loss and the transport of nutrients and sediments to downstream water bodies. 1
Implementation Considerations: Contour farming is most effective on slopes of 2% to 10% and 100 ft to 400 ft long. Stable outlets such as field borders and grassed waterways are necessary downstream components of contour farming. Contour farming improves the performance of downstream buffer-type practices such as contour buffer strips, terraces, contour strip-cropping, cover crop, filter strips, and grassed waterways because it helps to prevent concentrated flow.
Scalable to small farms? Yes
1 Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.; "Contour Farming." Natural Resources Conservation Service, Conservation Practice Standard. June 2007. Web. July 2014. http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs143_026017.pdf.
Practice Type: Structural, Management
Landuse/Agriculture Type: Row Crop, Small Grains, Fodder
Climatic Zones: Temperate, Semiarid, Tropical
Regions: North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia
Pollutants Treated: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sediment
Description: Contour farming entails farming along the contour such that ridges, furrows and planting are perpendicular to the slope of the land. The rows running across the slope are designed to be as level as possible to facilitate tillage and planting operations on the contour. Contour farming is an erosion control system that has the effect of increasing infiltration of rainwater and reducing sheet and rill erosion, thereby reducing soil loss and the transport of nutrients and sediments to downstream water bodies. 1
Implementation Considerations: Contour farming is most effective on slopes of 2% to 10% and 100 ft to 400 ft long. Stable outlets such as field borders and grassed waterways are necessary downstream components of contour farming. Contour farming improves the performance of downstream buffer-type practices such as contour buffer strips, terraces, contour strip-cropping, cover crop, filter strips, and grassed waterways because it helps to prevent concentrated flow.
Scalable to small farms? Yes
1 Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.; "Contour Farming." Natural Resources Conservation Service, Conservation Practice Standard. June 2007. Web. July 2014. http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs143_026017.pdf.
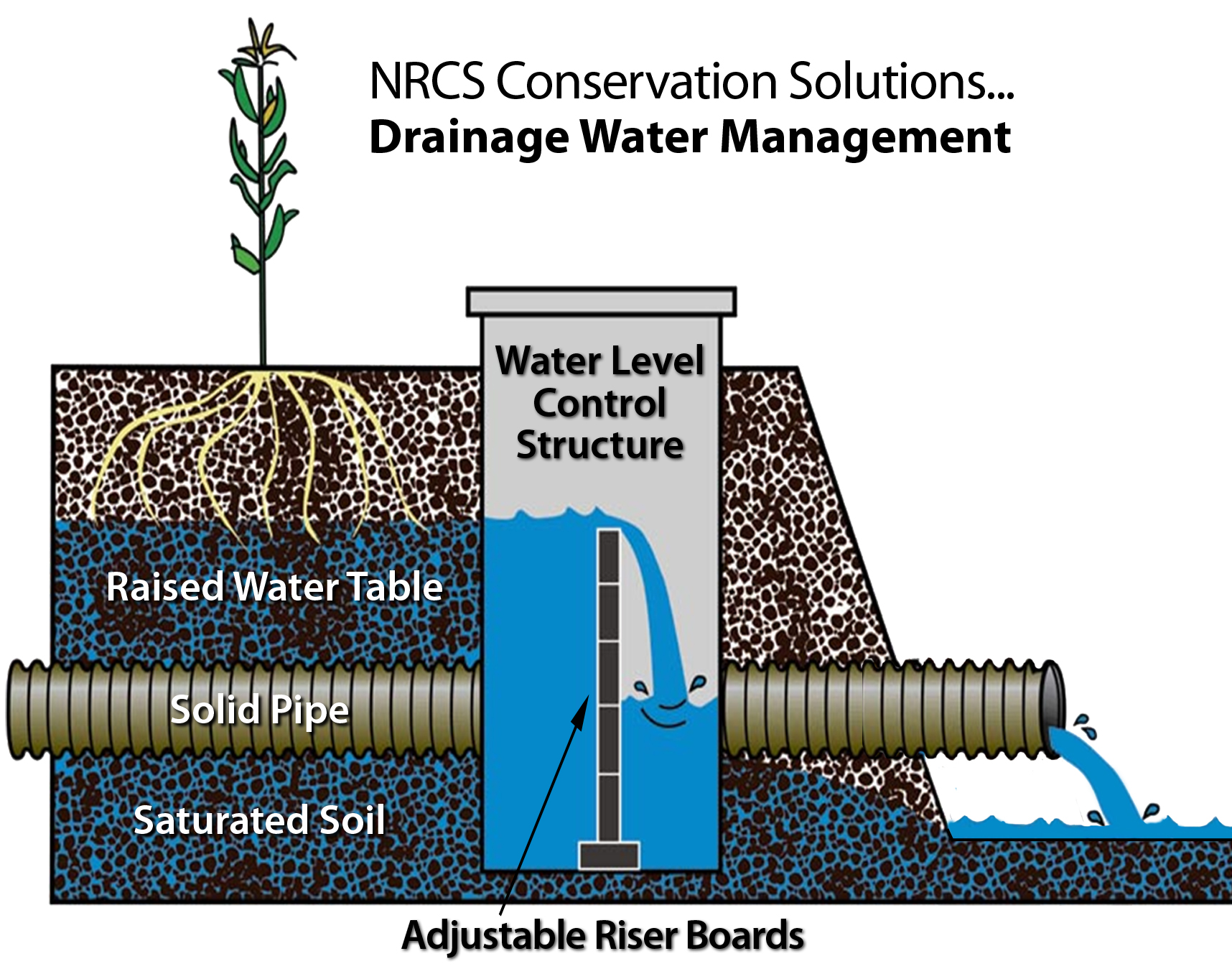
Controlled Drainage/Water Control Structures
Category: Drainage Control
Practice Type: Structural, Management
Landuse/Agriculture Type: Row Crop
Climatic Zones: Temperate, Tropical
Regions: North America, Europe
Pollutants Treated: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sediment
N Efficiency1: 61%
P Efficiency1: 50%
S Efficiency1: 63%
Description: Controlled drainage uses water control structures, such as a flashboard riser, installed in the drainage outlet, to allow the water in the drainage outlet to be raised or lowered as needed. When the flashboards are lowered or removed, subsurface drainage occurs more quickly, and when flashboards are added to the riser, the subsurface drainage rate is decreased and the height of the water level in the ditches and surrounding fields rises. Managing the field water through the use of controlled drainage allows timely drainage but also maximizes storage of water within a field for utilization by the crop. The transport of nitrogen from drained fields can be minimized by managing the drainage system such that only the minimum drainage water necessary is allowed to exit the field, and delivery of nitrates to surface waters is limited during critical times.2
Implementation Considerations: Generally, controlled drainage is better suited to flatter topography, since fewer water control structures are needed. The key operation consideration is when and by how much stoplogs are added or removed.
Scalable to small farms? Yes
Scaling Considerations: The use of subsurface tile drains is in a nascent state for small, limited resource farmers but surface ditches for drainage are used in many locations. Where surface drainage ditches are used -- for water management -- additional efforts could extend their value to nutrient management
1 Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.
2 "EU Database of Best Practices." Living Water Exchange: Promoting Replication of Good Practices for Nutrient Reduction and Joint Collaboration in Central and Eastern Europe. Web. Sept. 2013. http://nutrient2.iwlearn.org/nutrient-reduction-practices/eu-database-of-practices/view.; Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.
Practice Type: Structural, Management
Landuse/Agriculture Type: Row Crop
Climatic Zones: Temperate, Tropical
Regions: North America, Europe
Pollutants Treated: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sediment
N Efficiency1: 61%
P Efficiency1: 50%
S Efficiency1: 63%
Description: Controlled drainage uses water control structures, such as a flashboard riser, installed in the drainage outlet, to allow the water in the drainage outlet to be raised or lowered as needed. When the flashboards are lowered or removed, subsurface drainage occurs more quickly, and when flashboards are added to the riser, the subsurface drainage rate is decreased and the height of the water level in the ditches and surrounding fields rises. Managing the field water through the use of controlled drainage allows timely drainage but also maximizes storage of water within a field for utilization by the crop. The transport of nitrogen from drained fields can be minimized by managing the drainage system such that only the minimum drainage water necessary is allowed to exit the field, and delivery of nitrates to surface waters is limited during critical times.2
Implementation Considerations: Generally, controlled drainage is better suited to flatter topography, since fewer water control structures are needed. The key operation consideration is when and by how much stoplogs are added or removed.
Scalable to small farms? Yes
Scaling Considerations: The use of subsurface tile drains is in a nascent state for small, limited resource farmers but surface ditches for drainage are used in many locations. Where surface drainage ditches are used -- for water management -- additional efforts could extend their value to nutrient management
1 Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.
2 "EU Database of Best Practices." Living Water Exchange: Promoting Replication of Good Practices for Nutrient Reduction and Joint Collaboration in Central and Eastern Europe. Web. Sept. 2013. http://nutrient2.iwlearn.org/nutrient-reduction-practices/eu-database-of-practices/view.; Miller, T. P. , J. R. Peterson, C. F. Lenhart, and Y. Nomura. 2012. The Agricultural BMP Handbook for Minnesota. Minnesota Department of Agriculture.